Spawn a child process, given a vector of arguments
#include <process.h>
int spawnv( int mode,
const char * path,
char * const argv[] );
libc
The spawnv() function creates and executes a new child process, named in path with the NULL-terminated list of arguments in the argv vector.
The spawnv() function isn't a POSIX 1003.1 function, and isn't guaranteed to behave the same on all operating systems. It calls spawnve() before calling spawn().
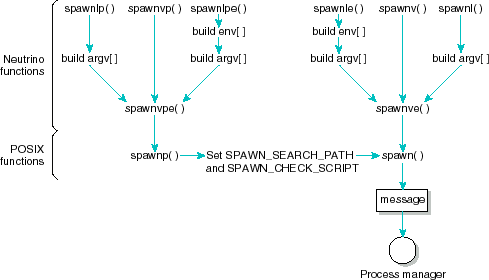
Most of the spawn*() functions do a lot of work before a message is sent to procnto.
The value of mode determines how the child process is loaded, and how the parent program behaves after the child program is initiated:
argv is a pointer to an argument vector. The value in argv[0] should point to a filename that is associated with the program being loaded. The last member of argv must be a NULL pointer. The value of argv can't be NULL, and argv[0] can't be a NULL pointer, even if no argument strings are passed.
The child process inherits the parent's environment. The environment is the collection of environment variables whose values that have been defined with the export shell command, the env utility, or by the successful execution of the putenv() or setenv() function. A program may read these values with the getenv() function.
| A parent/child relationship doesn't imply that the child process dies when the parent process dies. |
The spawnv() function's return value depends on the mode argument:
| mode | Return value |
|---|---|
| P_WAIT | The exit status of the child process. |
| P_NOWAIT | The process ID of the child process. To get the exit status for a P_NOWAIT process, you must use the waitpid() function, giving it this process ID. |
| P_NOWAITO | The process ID of the child process, or 0 if the process is being started on a remote node. You can't get the exit status of a P_NOWAITO process. |
If an error occurs, -1 is returned (errno is set).
Run myprog as if a user had typed:
myprog ARG1 ARG2
at the command-line:
#include <stddef.h>
#include <process.h>
char *arg_list[] = { "myprog", "ARG1", "ARG2", NULL };
...
spawnv( P_WAIT, "myprog", arg_list );
The program is found if myprog is in the current working directory.
| Safety: | |
|---|---|
| Cancellation point | Read the Caveats |
| Interrupt handler | No |
| Signal handler | No |
| Thread | Yes |
If mode is P_WAIT, this function is a cancellation point.
execl(), execle(), execlp(), execlpe(), execv(), execve(), execvp(), execvpe(), getenv(), putenv(), setenv(), spawn(), spawnve(), wait(), waitpid()